Understanding and collecting seeds of open-pollinated vegetables.
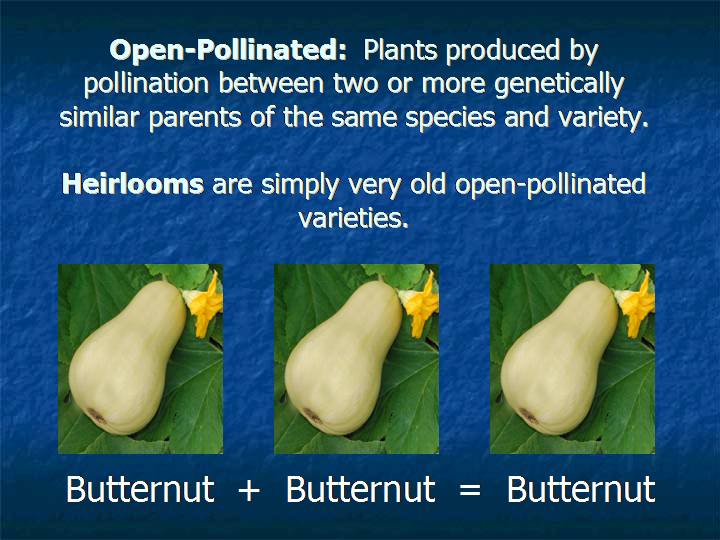
Open-pollinated seeds are a type of seeds that reproduce naturally through cross-pollination by agents such as wind, insects, and other animals. In contrast, closed-pollinated seeds are produced through controlled and selective pollination by farmers. The term "open pollination" refers to the way plants are fertilized through the transfer of pollen freely into the environment. These seeds are important for sustainable agriculture and the conservation of plant genetic diversity. In this article, we will explore in detail what open-pollinated seeds are, their importance in sustainable agriculture, how to select the right plants for collection, and how to properly collect and store these seeds. We will also discuss participating in seed exchanges and community events to encourage diversity and the benefits of engaging in open-pollinated seed saving.
- What are the open-pollinated seeds?
- Importance of open-pollinated seeds in sustainable agriculture
- Why is it important to understand and collect open-pollinated seeds?
- How to select the right plants for seed collection
- How to correctly collect and store open-pollinated seeds
- Participate in seed exchanges and community events to promote diversity
- Benefits of committing to open pollinated seed saving
- Conclusions and recommendations for starting to collect and understand open-pollinated seeds
What are the open-pollinated seeds?
Open-pollinated seeds are seeds that are produced through natural pollination, that is, by the transfer of pollen from one plant to another through natural means such as wind, insects and other animals. These seeds are the result of sexual reproduction of plants and can offer greater genetic diversity compared to closed-pollinated seeds.
Open-pollinated meaning
The term "open-pollinated" refers to the ability of plants to receive pollen from different sources, resulting in greater genetic diversity. By allowing plants to be open pollinated, mixing and recombination of genes is encouraged, which can result in plants with unique characteristics adapted to their environment.
What is open-pollinated seed?
An open-pollinated seed is one that is produced through natural pollination and results in progeny with similar characteristics to the parent plants. These seeds are not genetically engineered and are considered a more traditional and sustainable form of agriculture. By saving and replanting these seeds, farmers can maintain and promote the genetic diversity of the plants, as well as adapt them to local conditions.
What is an open-pollinated seed?
An open-pollinated seed is a seed produced by a plant that has been naturally pollinated by transferring pollen from other plants through agents such as wind, insects or animals. This type of pollination allows for greater genetic diversity and greater adaptation to local conditions. Open-pollinated seeds are fundamental to sustainable agriculture, as they allow farmers to save and replant their own seeds, promoting crop diversity and resilience.
Importance of open-pollinated seeds in sustainable agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is based on practices that promote resource conservation, biodiversity and environmental protection. Open-pollinated seeds play a vital role in sustainable agriculture because of their ability to maintain and promote plant genetic diversity.
Adequate genetic diversity allows plants to better adapt and resist environmental changes, such as diseases, pests, and climate change. In addition, genetic diversity is essential for long-term food security, as it ensures a greater variety of crops that can adapt to different growing conditions.
By growing open-pollinated seeds, farmers can maintain the genetic characteristics of plants that are best suited to their local environment. This means more resilient and healthier plants, which in turn reduces reliance on chemicals and promotes soil health and overall biodiversity.
In addition, open-pollinated seeds allow farmers to save and replant their own seeds, which means lower costs and greater autonomy. In contrast, hybrid or genetically modified seeds must be purchased each season, which can be costly and limiting for small-scale farmers.
Why is it important to understand and collect open-pollinated seeds?
Understanding and collecting open-pollinated seeds is important for several reasons. First, it allows farmers to preserve and promote the genetic diversity of cultivated plants. This is essential for long-term crop sustainability, as it ensures greater adaptability and resistance to diseases and changing environmental conditions.
Second, proper collection and storage of open-pollinated seeds ensures their viability and quality. By learning how to select the right plants for seed collection and how to properly collect and store seed, farmers can ensure they have a steady supply of healthy seeds for future crops.
In addition, understanding and collecting open-pollinated seeds promotes seed conservation and seed exchange among communities and gardening enthusiasts. Participating in seed exchanges and community events promotes diversity and connection with other individuals interested in sustainable agriculture. It also provides an opportunity to discover new varieties and share knowledge and experiences.
Understanding and collecting open-pollinated seeds is important to preserve plant genetic diversity, promote sustainability and crop resilience, ensure a steady supply of healthy seeds, and promote connection between communities and gardening enthusiasts.
How to select the right plants for seed collection
Selecting the right plants for seed collection is critical to obtaining healthy, viable seeds. Here are some key steps to follow:
1. Choose plants that are suitable for your growing conditions. Research what types of plants thrive in your region and climate. Consider factors such as temperature, soil type and sunlight availability.
2. Opt for plants that are resistant to diseases and pests. These plants will be more likely to produce healthy and resistant seeds.
3. Look for plants that have demonstrated good yields and desirable characteristics. This may include plants that produce tasty fruit, attractive flowers or hardy roots.
4. Avoid plants that are hybrids or genetically modified, as these will not produce open-pollinated seed. Instead, look for varieties that are described as "open or non-hybrid".
5. Consider genetic diversity when selecting your plants. Don't opt for just one variety, but several to promote diversity in your garden and ensure greater adaptability to environmental changes.
6. Make sure plants are well-fertilized and healthy before selecting them for seed collection. A healthy plant will produce stronger and healthier seeds.
Remember that selecting the right plants for seed collection is essential to obtaining high-quality, viable seed. Take the time to carefully research and choose the plants that will be the basis of your seed supply.
How to correctly collect and store open-pollinated seeds
Proper collection and storage are key to ensuring the viability and quality of open-pollinated seed. Here are some steps to follow:
1. Wait until the seeds are mature. This can be determined by observing the color change or hardening of the seeds. Avoid collecting immature seeds as they are not likely to be viable.
 Tips for Harvesting Blue Grey Oyster Mushrooms
Tips for Harvesting Blue Grey Oyster Mushrooms2. Remove seeds from plants carefully to avoid damaging them. In some plants, seeds are found in capsules or pods, while in others they may be inside fruits or flowers.
3. Clean and dry the seeds after collection. Remove any residue or plant matter adhering to the seeds and allow them to air dry in a cool, dry place.
4. Once dry, store the seeds in airtight containers and label them correctly with the name of the plant and date of collection. It is also useful to add additional information, such as growing conditions or any other relevant details.
5. Store seeds in a cool, dry place to avoid moisture and spoilage. A dark, refrigerated cupboard or shelf may be a good choice.
6. Check seeds periodically to make sure they are dry and in good condition. If you notice signs of moisture or deterioration, replace them with fresh seed.
Remember that each plant has its own specific recommendations for seed collection and storage. Do some research on the characteristics of the plants you are growing to make sure you are following the proper steps.
Participate in seed exchanges and community events to promote diversity
Participating in seed swaps and community events is a great way to promote diversity and connect with other gardening enthusiasts. These events offer the opportunity to exchange open-pollinated seeds with others and discover new plant varieties.
By participating in seed exchanges, you can expand your seed collection and try new plants in your garden. It also promotes genetic diversity and avoids dependence on commercial or genetically modified varieties.
In addition, community events related to gardening often offer workshops, educational talks, and opportunities to learn about sustainable food growing practices. This allows you to gain new knowledge and skills to improve your growing techniques and contribute to the sustainability of agriculture.
Participating in seed exchanges and community events is an exciting way to connect with other gardening enthusiasts, share experiences, and build lasting relationships. It also helps promote open-pollinated seed conservation and encourages diversity in our gardens and communities.
Benefits of committing to open pollinated seed saving
Committing to open-pollinated seed saving offers many benefits. Here are just a few of them:
Preservation of genetic diversity: The conservation of open-pollinated seeds allows for maintaining and promoting the genetic diversity of cultivated plants. This is essential for the adaptability and resistance of crops to environmental changes.
Increased autonomy and sustainability: By saving and replanting open-pollinated seeds, farmers can be more autonomous and sustainable. They are not dependent on the constant purchase of hybrid or genetically modified seeds, which can be costly and limiting.
3. Adaptability to local conditions: Locally grown open-pollinated seeds are more adaptable to local growing conditions. This means they are more resilient and healthier, which in turn reduces reliance on chemicals and promotes soil health and biodiversity.
4. Connecting with the community: Participating in seed swaps and community events fosters connection with other gardening enthusiasts and promotes the sharing of knowledge and experiences. This creates a strong community and supports the common goal of sustainability and conservation.
5. Contribution to food security: Open-pollinated seed conservation contributes to long-term food security. Crop diversity and seed adaptability promote resilience to challenges such as food shortages and climate change.
Committing to open-pollinated seed conservation has a number of benefits both for farmers and the wider community. It promotes genetic diversity, sustainability, self-reliance, and food security.
Conclusions and recommendations for starting to collect and understand open-pollinated seeds
Open-pollinated seeds play an important role in sustainable agriculture and biodiversity conservation. They are seeds that occur naturally through cross-pollination and allow for greater genetic diversity in crops.
Proper understanding and collection of these seeds is key to maintaining their viability and quality. By selecting the right plants, collecting mature seeds, cleaning and drying them properly, and storing them in optimal conditions, a continuous supply of healthy, viable seeds can be ensured.
Participating in seed swaps and community events is also a great way to promote diversity and connect with other gardening enthusiasts. These events offer the opportunity to exchange seeds, discover new varieties and learn about sustainable food growing practices.
Committing to open-pollinated seed conservation offers benefits such as preservation of genetic diversity, self-reliance, adaptability to local conditions, connection to the community, and contribution to food security.
If you are interested in starting to collect and understand open-pollinated seeds, we recommend researching more about the plants you want to grow and learning about best practices for collection and storage. We also encourage you to participate in seed exchanges and community events to connect with other enthusiasts and promote diversity in your garden and community.
Open-pollinated seed conservation is a valuable way to contribute to the sustainability and resilience of agriculture. By preserving genetic diversity and promoting crop adaptability, we are ensuring a healthier future for our communities and our planet.
 Maximize Your Planting Efficiency with Earthway Seed Plates
Maximize Your Planting Efficiency with Earthway Seed Plates
Leave a Reply